本文门槛较高,因此行文看起来会乱一些,如果你看到某处能会心一笑请马上联系我开始摆龙门阵
如果你跟随这篇文章实现了播放器,那你会得到一个高效率,低cpu占用(单路720p视频解码播放占用1%左右cpu),且代码和引用精简(无其他托管和非托管的dll依赖,更无需安装任何插件,你的程序完全绿色运行);并且如果硬解不可用,切换到软件是自动过程
首先需要准备好visual studio/msys2/ffmpeg源码/dx9sdk。因为我们要自己编译ffmpeg,并且是改动代码后编译,ffmpeg我们编译时会裁剪。
ffmpeg源码大家使用4.2.1,和我保持同步,这样比较好对应,下载地址为ffmpeg-4.2.1.tar.gz
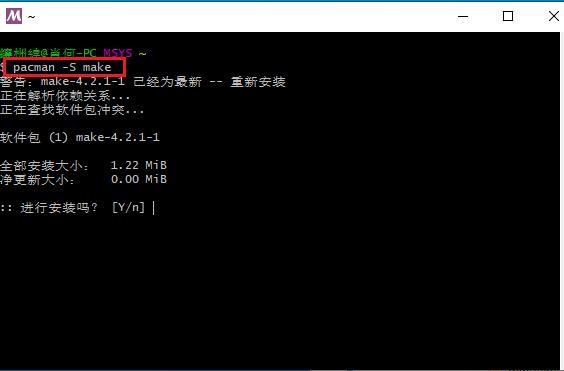
msys2安装好后不需要装mingw和其他东西,只需要安装make(见下方图片;我们编译工具链会用msvc而非mingw-gcc)
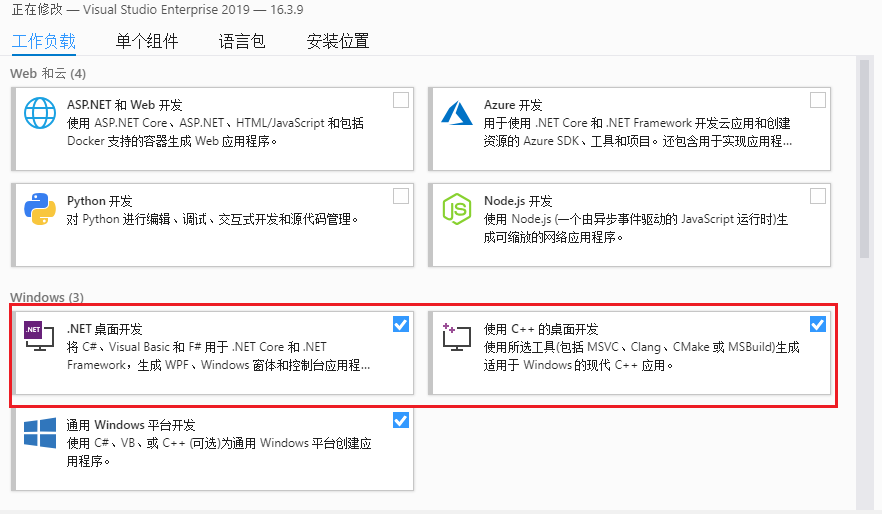
visual studio版本按道理是不需要新版本的,应该是2008-2019都可以(不过还是得看看ffmpeg代码里是否用了c99 c11等低版本不支持的东西),vs需要安装c++和c#的模块(见下方图片;应该也不需要特意去打开什么功能)
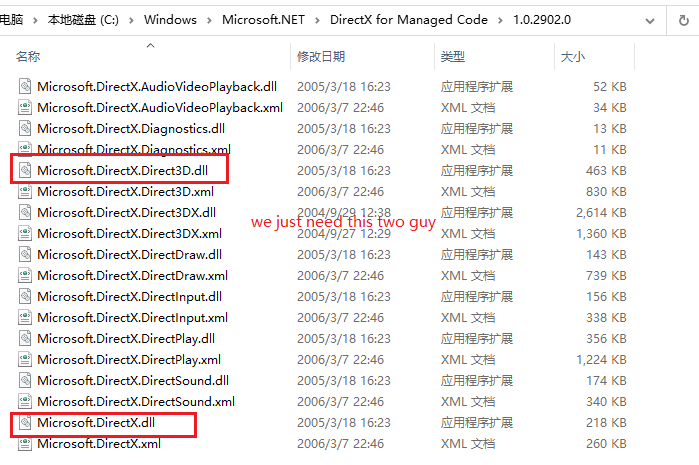
dx9的sdk理论上是不用安装的(如果你是高手,可以用c#的ilgenerator直接写calli;亦或者写unsafe代码直接进行内存call,文章最后我会为大家揭秘如何用c#调用c++甚至com组件)。我用了directx的managecode,由官方为我们做了dx的调用(见下方图片)
第二步是修改ffmpeg源码并编译,我们要修改的源码只有一个文件的十余行,而且是增量修改。
修改的文件位于libavutil/hwcontext_dxva2.c文件,我先将修改部分贴出来然后再给大家解释
static int dxva2_device_create9_extend(AVHWDeviceContext ctx, UINT adapter, HWND hWnd)
{
DXVA2DevicePriv priv = ctx->user_opaque;
D3DPRESENT_PARAMETERS d3dpp = {0};
D3DDISPLAYMODE d3ddm;
HRESULT hr;
pDirect3DCreate9 createD3D = (pDirect3DCreate9 )dlsym(priv->d3dlib, "Direct3DCreate9");
if (!createD3D) {
av_log(ctx, AV_LOG_ERROR, "Failed to locate Direct3DCreate9n");
return AVERROR_UNKNOWN;
}priv->d3d9 = createD3D(D3D_SDK_VERSION);
if (!priv->d3d9) {
av_log(ctx, AV_LOG_ERROR, "Failed to create IDirect3D objectn");
return AVERROR_UNKNOWN;
}
IDirect3D9_GetAdapterDisplayMode(priv->d3d9, adapter, &d3ddm);
d3dpp.BackBufferFormat = d3ddm.Format;
d3dpp.Windowed = TRUE; // 是否窗口显示
d3dpp.hDeviceWindow = hWnd; // 显示窗口句柄
d3dpp.SwapEffect = D3DSWAPEFFECT_DISCARD; // 交换链设置,后台缓冲使用后直接丢弃
d3dpp.Flags = D3DPRESENTFLAG_VIDEO; // 附加特性,显示视频
DWORD behaviorFlags = D3DCREATE_MULTITHREADED | D3DCREATE_FPU_PRESERVE;
D3DDEVTYPE devType = D3DDEVTYPE_HAL;
D3DCAPS9 caps;
if (IDirect3D9_GetDeviceCaps(priv->d3d9, D3DADAPTER_DEFAULT, devType, &caps) >= 0)
{
if (caps.DevCaps & D3DDEVCAPS_HWTRANSFORMANDLIGHT)
{
behaviorFlags |= D3DCREATE_HARDWARE_VERTEXPROCESSING;
}
else
{
behaviorFlags |= D3DCREATE_SOFTWARE_VERTEXPROCESSING;
}
}
if(!hWnd)
hWnd = GetDesktopWindow();
hr = IDirect3D9_CreateDevice(priv->d3d9, adapter, D3DDEVTYPE_HAL, hWnd,
behaviorFlags,
&d3dpp, &priv->d3d9device);
if (FAILED(hr)) {
av_log(ctx, AV_LOG_ERROR, "Failed to create Direct3D devicen");
return AVERROR_UNKNOWN;
}
return 0;
}
static int dxva2_device_create(AVHWDeviceContext ctx, const char device,
AVDictionary opts, int flags)
{
AVDXVA2DeviceContext hwctx = ctx->hwctx;
DXVA2DevicePriv priv;
pCreateDeviceManager9 createDeviceManager = NULL;
unsigned resetToken = 0;
UINT adapter = D3DADAPTER_DEFAULT;
HRESULT hr;
int err;
AVDictionaryEntry *t = NULL;
HWND hWnd = NULL;
if (device)
adapter = atoi(device);
priv = av_mallocz(sizeof(*priv));
if (!priv)
return AVERROR(ENOMEM);
ctx->user_opaque = priv;
ctx->free = dxva2_device_free;
priv->device_handle = INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE;
priv->d3dlib = dlopen("d3d9.dll", 0);
if (!priv->d3dlib) {
av_log(ctx, AV_LOG_ERROR, "Failed to load D3D9 libraryn");
return AVERROR_UNKNOWN;
}
priv->dxva2lib = dlopen("dxva2.dll", 0);
if (!priv->dxva2lib) {
av_log(ctx, AV_LOG_ERROR, "Failed to load DXVA2 libraryn");
return AVERROR_UNKNOWN;
}
createDeviceManager = (pCreateDeviceManager9 *)dlsym(priv->dxva2lib,
"DXVA2CreateDirect3DDeviceManager9");
if (!createDeviceManager) {
av_log(ctx, AV_LOG_ERROR, "Failed to locate DXVA2CreateDirect3DDeviceManager9n");
return AVERROR_UNKNOWN;
}
t = av_dict_get(opts, "hWnd", NULL, 0);
if(t) {
hWnd = (HWND)atoi(t->value);
}
if(hWnd) {
if((err = dxva2_device_create9_extend(ctx, adapter, hWnd)) < 0)
return err;
} else {
if (dxva2_device_create9ex(ctx, adapter) < 0) {
// Retry with "classic" d3d9
err = dxva2_device_create9(ctx, adapter);
if (err < 0)
return err;
}
}
hr = createDeviceManager(&resetToken, &hwctx->devmgr);
if (FAILED(hr)) {
av_log(ctx, AV_LOG_ERROR, "Failed to create Direct3D device managern");
return AVERROR_UNKNOWN;
}
hr = IDirect3DDeviceManager9_ResetDevice(hwctx->devmgr, priv->d3d9device, resetToken);
if (FAILED(hr)) {
av_log(ctx, AV_LOG_ERROR, "Failed to bind Direct3D device to device managern");
return AVERROR_UNKNOWN;
}
hr = IDirect3DDeviceManager9_OpenDeviceHandle(hwctx->devmgr, &priv->device_handle);
if (FAILED(hr)) {
av_log(ctx, AV_LOG_ERROR, "Failed to open device handlen");
return AVERROR_UNKNOWN;
}
return 0;
}
代码中dxva2_device_create9_extend函数是我新加入的,并且在dxva2_device_create函数(这个函数是ffmpeg原始流程中的,我的改动不影响原本任何功能)中适时调用;简单来说,原来的ffmpeg也能基于dxva2硬件解码,但是它没法将解码得到的surface用于前台播放,因为它创建device时并未指定窗口和其他相关参数,大家可以参考我代码实现,我将窗口句柄传入后创建过程完全改变(其他人如果使用我们编译的代码,他没有传入窗口句柄,就执行原来的创建,因此百分百兼容)。
(ps:在这里我讲一下网络上另外一种写法(两年前我也用的他们的,因为没时间详细看ffmpeg源码),他们是在外面创建的device和surface然后想办法传到ffmpeg内部进行替换,这样做有好处,就是不用自己修改和编译ffmpeg,坏处是得自己维护device和surface。至于二进制兼容方面考虑,两种做法都不是太好)
代码修改完成后我们使用msys2编译
首先是需要把编译器设置为msvc,这个步骤通过使用vs的命令行工具即可,如下图

然后是设置msys2继承环境变量(这样make时才能找到cl/link)
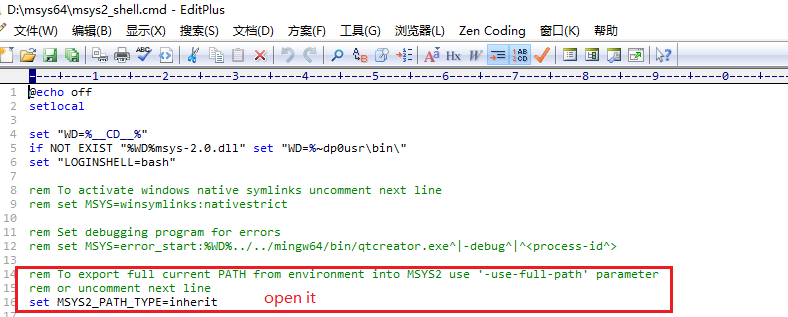
打开msys,查看变量是否正确

编译ffmpeg
./configure --enable-shared --enable-small --disable-all --disable-autodetect --enable-avcodec --enable-decoder=h264 --enable-dxva2 --enable-hwaccel=h264_dxva2 --toolchain=msvc --prefix=host make && make install
编译完成后头文件和dll在host文件夹内(编译产出的dll也是clear的,不依赖msvc**.dll)
在C#中使用我们产出的方式需要使用p/invoke和unsafe代码。
我先贴出我针对ffmpeg写的一个工具类,然后给大家稍微讲解一下
using System;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
namespace MultiPlayer
{
public enum AVCodecID
{
AV_CODEC_ID_NONE,
/* video codecs */
AV_CODEC_ID_MPEG1VIDEO,
AV_CODEC_ID_MPEG2VIDEO, ///
/// ffmpeg中AVFrame结构体的前半部分,因为它太长了我不需要完全移植过来
///
[StructLayout(LayoutKind.Sequential, Pack = 1, Size = 408)]
public struct AVFrame
{
//#define AV_NUM_DATA_POINTERS 8
// uint8_t* data[AV_NUM_DATA_POINTERS];
public IntPtr data1;// 一般是y分量
public IntPtr data2;// 一般是v分量
public IntPtr data3;// 一般是u分量
public IntPtr data4;// 一般是surface(dxva2硬解时)
public IntPtr data5;
public IntPtr data6;
public IntPtr data7;
public IntPtr data8;
public int linesize1;// y分量每行长度(stride)
public int linesize2;// v分量每行长度(stride)
public int linesize3;// u分量每行长度(stride)
public int linesize4;
public int linesize5;
public int linesize6;
public int linesize7;
public int linesize8;
//uint8_t **extended_data;
IntPtr extended_data;
public int width;
public int height;
public int nb_samples;
public AVPixelFormat format;
}
[StructLayout(LayoutKind.Sequential, Pack = 1, Size = 128)]
public struct AVCodec { }
[StructLayout(LayoutKind.Sequential, Pack = 1, Size = 72)]
public unsafe struct AVPacket
{
fixed byte frontUnused[24]; // 前部无关数据
public void* data;
public int size;
}
[StructLayout(LayoutKind.Sequential, Pack = 1, Size = 12)]
public struct AVBufferRef { }
[StructLayout(LayoutKind.Sequential, Pack = 1, Size = 904)]
public unsafe struct AVCodecContext
{
fixed byte frontUnused[880]; // 前部无关数据
public AVBufferRef* hw_frames_ctx;
}
[StructLayout(LayoutKind.Sequential)]
public struct AVDictionary { }
public unsafe static class FFHelper
{
const string avcodec = "avcodec-58";
const string avutil = "avutil-56";
const CallingConvention callingConvention = CallingConvention.Cdecl;
[DllImport(avcodec, CallingConvention = callingConvention)]
public extern static void avcodec_register_all();
[DllImport(avcodec, CallingConvention = callingConvention)]
public extern static AVCodec* avcodec_find_decoder(AVCodecID id);
[DllImport(avcodec, CallingConvention = callingConvention)]
public extern static AVPacket* av_packet_alloc();
[DllImport(avcodec, CallingConvention = callingConvention)]
public extern static void av_init_packet(AVPacket* pkt);
//[DllImport(avcodec, CallingConvention = callingConvention)]
//public extern static void av_packet_unref(AVPacket* pkt);
[DllImport(avcodec, CallingConvention = callingConvention)]
public extern static void av_packet_free(AVPacket** pkt);
[DllImport(avcodec, CallingConvention = callingConvention)]
public extern static AVCodecContext* avcodec_alloc_context3(AVCodec* codec);
[DllImport(avcodec, CallingConvention = callingConvention)]
public extern static int avcodec_open2(AVCodecContext* avctx, AVCodec* codec, AVDictionary** options);
//[DllImport(avcodec, CallingConvention = callingConvention)]
//public extern static int avcodec_decode_video2(IntPtr avctx, IntPtr picture, ref int got_picture_ptr, IntPtr avpkt);
[DllImport(avcodec, CallingConvention = callingConvention)]
public extern static void avcodec_free_context(AVCodecContext** avctx);
[DllImport(avcodec, CallingConvention = callingConvention)]
public extern static int avcodec_send_packet(AVCodecContext* avctx, AVPacket* pkt);
[DllImport(avcodec, CallingConvention = callingConvention)]
public extern static int avcodec_receive_frame(AVCodecContext* avctx, AVFrame* frame);
[DllImport(avutil, CallingConvention = callingConvention)]
public extern static int av_hwdevice_ctx_create(AVBufferRef** device_ctx, AVHWDeviceType type, string device, AVDictionary* opts, int flags);
[DllImport(avutil, CallingConvention = callingConvention)]
public extern static AVBufferRef* av_buffer_ref(AVBufferRef* buf);
[DllImport(avutil, CallingConvention = callingConvention)]
public extern static void av_buffer_unref(AVBufferRef** buf);
[DllImport(avutil, CallingConvention = callingConvention)]
public extern static AVFrame* av_frame_alloc();
[DllImport(avutil, CallingConvention = callingConvention)]
public extern static void av_frame_free(AVFrame** frame);
[DllImport(avutil, CallingConvention = callingConvention)]
public extern static void av_log_set_level(int level);
[DllImport(avutil, CallingConvention = callingConvention)]
public extern static int av_dict_set_int(AVDictionary** pm, string key, long value, int flags);
[DllImport(avutil, CallingConvention = callingConvention)]
public extern static void av_dict_free(AVDictionary** m);
}
}上文中主要有几个地方是知识点,大家做c#的如果需要和底层交互可以了解一下
结构体的使用
结构体在c#与c/c++基本一致,都是内存连续变量的一种组合方式。与c/c++相同,在c#中,如果我们不知道(或者可以规避,因为结构体可能很复杂,很多无关字段)结构体细节只知道结构体整体大小时,我们可以用Pack=1,SizeConst=来表示一个大小已知的结构体。指针的使用
c#中,有两种存储内存地址(指针)的方式,一是使用interop体系中的IntPtr类型(大家可以将其想象成void*),一是在不安全的上下文(unsafe)中使用结构体类型指针(此处不讨论c++类指针)unsafe和fixed使用
简单来说,有了unsafe你才能用指针;而有了fixed你才能确保指针指向位置不被GC压缩。我们使用fixed达到的效果就是显式跳过了结构体中前部无关数据(参考上文中AVCodecContext等结构体定义),后文中我们还会使用fixed。
现在我们开始编写解码和播放部分(即我们的具体应用)代码
using Microsoft.DirectX;
using Microsoft.DirectX.Direct3D;
using System;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
using System.Text;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using static MultiPlayer.FFHelper;namespace MultiPlayer
{
public unsafe partial class FFPlayer : UserControl
{
[DllImport("msvcrt", EntryPoint = "memcpy", CallingConvention = CallingConvention.Cdecl, SetLastError = false)]
static extern void memcpy(IntPtr dest, IntPtr src, int count); // 用于在解码器和directx间拷贝内存的c函数
private IntPtr contentPanelHandle; // 画面渲染的控件句柄,因为画面渲染时可能出于非UI线程,因此先保存句柄避免CLR报错
private int lastIWidth, lastIHeight; // 上次控件大小,用于在控件大小改变时做出判定重新初始化渲染上下文
private Rectangle lastCBounds; // 临时变量,存储上次控件区域(屏幕坐标)
private Rectangle lastVRect; // 临时变量,存储上次解码出的图像大小
private Device device; // 当使用软解时,这个变量生效,它是IDirect3Device9*对象,用于绘制YUV
private Surface surface; // 当使用软解时,这个变量生效,它是IDirect3Surface9*对象,用于接受解码后的YUV数据
AVPixelFormat lastFmt; // 上次解码出的图像数据类型,这个理论上不会变
AVCodec* codec; // ffmpeg的解码器
AVCodecContext* ctx; // ffmpeg的解码上下文
AVBufferRef* hw_ctx; // ffmpeg的解码器硬件加速上下文,作为ctx的扩展存在
AVPacket* avpkt; // ffmpeg的数据包,用于封送待解码数据
IntPtr nalData; // 一块预分配内存,作为avpkt中真正存储数据的内存地址
AVFrame* frame; // ffmpeg的已解码帧,用于回传解码后的图像
private volatile bool _released = false; // 资源释放标识,与锁配合使用避免重复释放资源(由于底层是c/c++,多线程下double free会导致程序崩溃)
private object _codecLocker = new object(); // 锁,用于多线程下的互斥
static FFPlayer()
{
avcodec_register_all(); // 静态块中注册ffmpeg解码器
}
public FFPlayer()
{
InitializeComponent();
// 过程中,下列对象只需初始化一次
frame = av_frame_alloc();
avpkt = av_packet_alloc();
av_init_packet(avpkt);
nalData = Marshal.AllocHGlobal(1024 * 1024);
codec = avcodec_find_decoder(AVCodecID.AV_CODEC_ID_H264);
avpkt->data = (void*)nalData;
}
~FFPlayer()
{
// 过程中,下列对象只需释放一次
if (null != frame)
fixed (AVFrame** LPframe = &frame)
av_frame_free(LPframe);
if (null != avpkt)
fixed (AVPacket** LPpkt = &avpkt)
av_packet_free(LPpkt);
if (default != nalData)
Marshal.FreeHGlobal(nalData);
}
// 释放资源
// 此函数并非表示“终止”,更多的是表示“改变”和“重置”,实际上对此函数的调用更多的是发生在界面大小发生变化时和网络掉包导致硬解异常时
private void Releases()
{
// 过程中,下列对象会重复创建和销毁多次
lock (_codecLocker)
{
if (_released) return;
if (null != ctx)
fixed (AVCodecContext** LPctx = &ctx)
avcodec_free_context(LPctx);
if (null != hw_ctx)
fixed (AVBufferRef** LPhw_ctx = &hw_ctx)
av_buffer_unref(LPhw_ctx);
// (PS:device和surface我们将其置为null,让GC帮我们调用Finalize,它则会自行释放资源)
surface = null;
device = null;
lastFmt = AVPixelFormat.AV_PIX_FMT_NONE;
_released = true;
}
}
// Load事件中保存控件句柄
private void FFPlayer_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
contentPanelHandle = Handle; // 这个句柄也可以是你控件内真正要渲染画面的句柄
lastCBounds = ClientRectangle; // 同理,区域也不一定是自身显示区域
}
// 解码函数,由外部调用,送一一个分片好的nal
public void H264Received(byte[] nal)
{
lock (_codecLocker)
{
// 判断界面大小更改了,先重置一波
// (因为DirectX中界面大小改变是一件大事,没得法绕过,只能推倒从来)
// 如果你的显示控件不是当前控件本身,此处需要做修改
if (!ClientRectangle.Equals(lastCBounds))
{
lastCBounds = ClientRectangle;
Releases();
}
if (null == ctx)
{
// 第一次接收到待解码数据时初始化一个解码器上下文
ctx = avcodec_alloc_context3(codec);
if (null == ctx)
{
return;
}
// 通过参数传递控件句柄给硬件加速上下文
AVDictionary* dic;
av_dict_set_int(&dic, "hWnd", contentPanelHandle.ToInt64(), 0);
fixed (AVBufferRef** LPhw_ctx = &hw_ctx)
{
if (av_hwdevice_ctx_create(LPhw_ctx, AVHWDeviceType.AV_HWDEVICE_TYPE_DXVA2,
null, dic, 0) >= 0)
{
ctx->hw_frames_ctx = av_buffer_ref(hw_ctx);
}
}
av_dict_free(&dic);
ctx->hw_frames_ctx = av_buffer_ref(hw_ctx);
if (avcodec_open2(ctx, codec, null) < 0)
{
fixed (AVCodecContext** LPctx = &ctx)
avcodec_free_context(LPctx);
fixed (AVBufferRef** LPhw_ctx = &hw_ctx)
av_buffer_unref(LPhw_ctx);
return;
}
}
_released = false;
// 开始解码
Marshal.Copy(nal, 0, nalData, nal.Length);
avpkt->size = nal.Length;
if (avcodec_send_packet(ctx, avpkt) < 0)
{
Releases(); return; // 如果程序走到了这里,一般是因为网络掉包导致nal数据不连续,没办法, 推倒从来
}
receive_frame:
int err = avcodec_receive_frame(ctx, frame);
if (err == -11) return; // EAGAIN
if (err < 0)
{
Releases(); return; // 同上,一般这里很少出错,但一旦发生,只能推倒从来
}
// 尝试播放一帧画面
AVFrame s_frame = *frame;
// 这里由于我无论如何都要加速,而一般显卡最兼容的是yv12格式,因此我只对dxva2和420p做了处理,如果你的h264解出来不是这些,我建议转成rgb(那你就需要编译和使用swscale模块了)
if (s_frame.format != AVPixelFormat.AV_PIX_FMT_DXVA2_VLD && s_frame.format != AVPixelFormat.AV_PIX_FMT_YUV420P && s_frame.format != AVPixelFormat.AV_PIX_FMT_YUVJ420P) return;
try
{
int width = s_frame.width;
int height = s_frame.height;
if (lastIWidth != width || lastIHeight != height || lastFmt != s_frame.format) // 这个if判定的是第一次尝试渲染,因为一般码流的宽高和格式不会变
{
if (s_frame.format != AVPixelFormat.AV_PIX_FMT_DXVA2_VLD)
{
// 假如硬解不成功(例如h264是baseline的,ffmpeg新版不支持baseline的dxva2硬解)
// 我们就尝试用directx渲染yuv,至少省去yuv转rgb,可以略微节省一丢丢cpu
PresentParameters pp = new PresentParameters();
pp.Windowed = true;
pp.SwapEffect = SwapEffect.Discard;
pp.BackBufferCount = 0;
pp.DeviceWindowHandle = contentPanelHandle;
pp.BackBufferFormat = Manager.Adapters.Default.CurrentDisplayMode.Format;
pp.EnableAutoDepthStencil = false;
pp.PresentFlag = PresentFlag.Video;
pp.FullScreenRefreshRateInHz = 0;//D3DPRESENT_RATE_DEFAULT
pp.PresentationInterval = 0;//D3DPRESENT_INTERVAL_DEFAULT
Caps caps = Manager.GetDeviceCaps(Manager.Adapters.Default.Adapter, DeviceType.Hardware);
CreateFlags behaviorFlas = CreateFlags.MultiThreaded | CreateFlags.FpuPreserve;
if (caps.DeviceCaps.SupportsHardwareTransformAndLight)
{
behaviorFlas |= CreateFlags.HardwareVertexProcessing;
}
else
{
behaviorFlas |= CreateFlags.SoftwareVertexProcessing;
}
device = new Device(Manager.Adapters.Default.Adapter, DeviceType.Hardware, contentPanelHandle, behaviorFlas, pp);
//(Format)842094158;//nv12
surface = device.CreateOffscreenPlainSurface(width, height, (Format)842094169, Pool.Default);//yv12,显卡兼容性最好的格式
}
lastIWidth = width;
lastIHeight = height;
lastVRect = new Rectangle(0, 0, lastIWidth, lastIHeight);
lastFmt = s_frame.format;
}
if (lastFmt != AVPixelFormat.AV_PIX_FMT_DXVA2_VLD)
{
// 如果硬解失败,我们还需要把yuv拷贝到surface
//ffmpeg没有yv12,只有i420,而一般显卡又支持的是yv12,因此下文中uv分量是反向的
int stride;
var gs = surface.LockRectangle(LockFlags.DoNotWait, out stride);
if (gs == null) return;
for (int i = 0; i < lastIHeight; i++)
{
memcpy(gs.InternalData + i * stride, s_frame.data1 + i * s_frame.linesize1, lastIWidth);
}
for (int i = 0; i < lastIHeight / 2; i++)
{
memcpy(gs.InternalData + stride * lastIHeight + i * stride / 2, s_frame.data3 + i * s_frame.linesize3, lastIWidth / 2);
}
for (int i = 0; i < lastIHeight / 2; i++)
{
memcpy(gs.InternalData + stride * lastIHeight + stride * lastIHeight / 4 + i * stride / 2, s_frame.data2 + i * s_frame.linesize2, lastIWidth / 2);
}
surface.UnlockRectangle();
}
// 下面的代码开始烧脑了,如果是dxva2硬解出来的图像数据,则图像数据本身就是一个surface,并且它就绑定了device
// 因此我们可以直接用它,如果是x264软解出来的yuv,则我们需要用上文创建的device和surface搞事情
Surface _surface = lastFmt == AVPixelFormat.AV_PIX_FMT_DXVA2_VLD ? new Surface(s_frame.data4) : surface;
if (lastFmt == AVPixelFormat.AV_PIX_FMT_DXVA2_VLD)
GC.SuppressFinalize(_surface);// 这一句代码是点睛之笔,如果不加,程序一会儿就崩溃了,熟悉GC和DX的童鞋估计一下就能看出门道;整篇代码,就这句折腾了我好几天,其他都好说
Device _device = lastFmt == AVPixelFormat.AV_PIX_FMT_DXVA2_VLD ? _surface.Device : device;
_device.Clear(ClearFlags.Target, Color.Black, 1, 0);
_device.BeginScene();
Surface backBuffer = _device.GetBackBuffer(0, 0, BackBufferType.Mono);
_device.StretchRectangle(_surface, lastVRect, backBuffer, lastCBounds, TextureFilter.Linear);
_device.EndScene();
_device.Present();
backBuffer.Dispose();
}
catch (DirectXException ex)
{
StringBuilder msg = new StringBuilder();
msg.Append("*************************************** n");
msg.AppendFormat(" 异常发生时间: {0} n", DateTime.Now);
msg.AppendFormat(" 导致当前异常的 Exception 实例: {0} n", ex.InnerException);
msg.AppendFormat(" 导致异常的应用程序或对象的名称: {0} n", ex.Source);
msg.AppendFormat(" 引发异常的方法: {0} n", ex.TargetSite);
msg.AppendFormat(" 异常堆栈信息: {0} n", ex.StackTrace);
msg.AppendFormat(" 异常消息: {0} n", ex.Message);
msg.Append("***************************************");
Console.WriteLine(msg);
Releases();
return;
}
goto receive_frame; // 尝试解出第二幅画面(实际上不行,因为我们约定了单次传入nal是一个,当然,代码是可以改的)
}
}
// 外部调用停止解码以显示释放资源
public void Stop()
{
Releases();
}
}
}
下面讲解代码最主要的三个部分
初始化ffmpeg
主要在静态块和构造函数中,过程中我没有将AVPacket和AVFrame局部化,很多网上的代码包括官方代码都是局部化这两个对象。我对此持保留意见(等我程序报错了再说)将收到的数据送入ffmpeg解码并将拿到的数据进行展示
这里值得一提的是get_format,官方有一个示例,下图
它有一个get_format过程(详见215行和63行),我没有采用。这里给大家解释一下原因:
这个get_format的作用是ffmpeg给你提供了多个解码器让你来选一个,而且它内部有一个机制,如果你第一次选的解码器不生效(初始化错误等),它会调用get_format第二次(第三次。。。)让你再选一个,而我们首先认定了要用dxva2的硬件解码器,其次,如果dxva2初始化错误,ffmpeg内部会自动降级为内置264软解,因此我们无需多此一举。
发现解码和播放过程中出现异常的解决办法
不支持硬解
代码中已经做出了一部分兼容,因为baseline的判定必须解出sps/pps才能知道,因此这个错误可能会延迟爆出(不过不用担心,如果此时报错,ffmpeg会自动降级为软解)窗体大小改变
基于DirectX中设备后台缓冲的宽高无法动态重设,我们只能在控件大小改变时推倒重来。如若不然,你绘制的画面会进行意向不到的缩放网络掉包导致硬件解码器错误
见代码其他directx底层异常
代码中我加了一个try-catch,捕获的异常类型是DirectXException,在c/c++中,我们一般是调用完函数后会得到一个HRESULT,并通过FAILED宏判定他,而这个步骤在c#自动帮我们做了,取而代之的是一个throw DirectXException过程,我们通过try-catch进行可能的异常处理(实际上还是推倒重来)
番外篇:C#对DiretX调用的封装
上文中我们使用DirectX的方式看起来即非COM组件,又非C-DLL的P/Invoke,难道DirectX真有托管代码?
答案是否定的,C#的dll当然也是调用系统的d3d9.dll。不过我们有必要一探究竟,因为这里面有一个隐藏副本
首先请大家准备好ildasm和visual studio,我们打开visual studio,创建一个c++工程(类型随意),然后新建一个cpp文件,然后填入下面的代码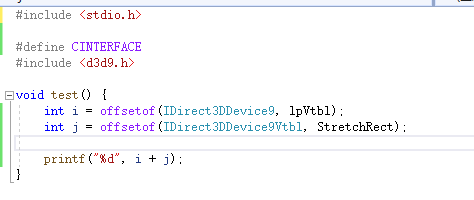
如果你能执行,你会发现输出是88;然后我们使用ildasm找到StrechRectangle的代码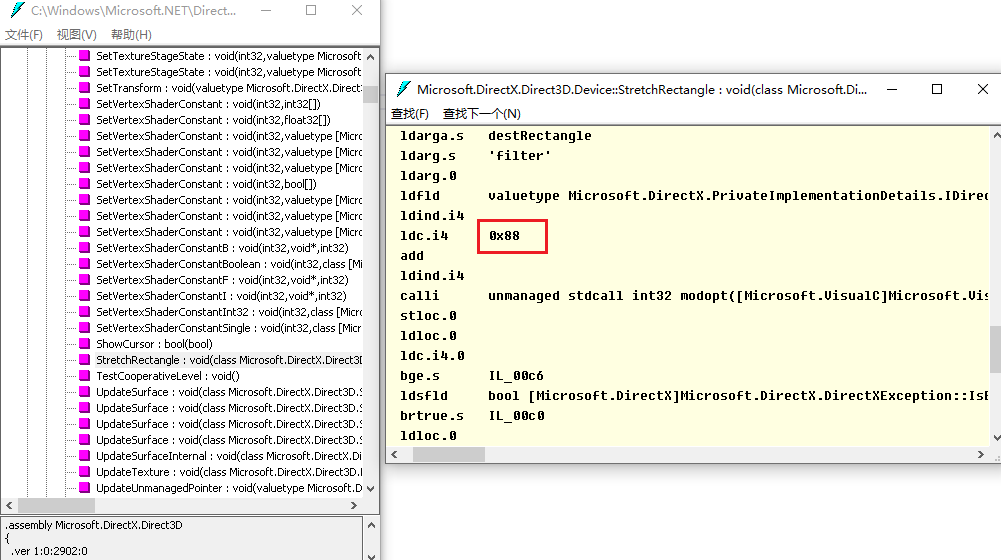
你会发现也有一个+88的过程,那么其实道理就很容易懂了,c#通过calli(CLR指令)可以执行内存call,而得益于微软com组件的函数表偏移量约定,我们可以通过头文件知道函数对于对象指针的偏移(其实就是一个简单的ThisCall)。具体细节大家查阅d3d9.h和calli的网络文章即可.


